Okay, so your boss wants to understand what the heck is going on with his manufacturing systems and make sure that YOU can prevent any “hiccups” before they happen. Well, that’s easier said than done, right? Especially when you’re manufacturing complex products that could potentially require thousands of parts from hundreds of suppliers. So, where do you start when you need to ensure that your manufacturing process runs as smoothly as possible without any surprises? Start with the basics.
What is Process Failure Modes and Effect Analysis (PFMEA)?
Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is a systematic, proactive method of evaluating a process. A PFMEA identifies the opportunities for failure, or “failure modes,” in each step of the process. “Failure modes” refers to the ways, or modes, in which something might fail. Failures are any errors or defects, especially ones that affect the customer or the products being built, and they can be potential or actual. Each failure mode gets a numeric score that quantifies:
- the likelihood that the failure will occur (the occurrence of the potential failure)
- the likelihood that the failure will not be detected (the detection of the potential failure) and
- the amount of harm or damage the failure mode may cause to a person or to equipment (the severity of the potential failure).
The product of these three scores is the Risk Priority Number (RPN) for that failure mode. The sum of all the RPNs for the failure modes is the overall RPN for the process. As an organization works to improve a process, it can anticipate and compare the effects of proposed changes by calculating hypothetical RPNs for different scenarios. Just remember that the RPN is a measure for comparisons within one process only; it is not a measure for comparing risk between processes or organizations.
When Do I Use PFMEA?
- When a new process is being put into place
- When an existing process or product is being applied in a new way
- Before developing control plans for a new or modified process
- When improvement goals are planned for an existing process, product or service
- When analyzing failures of an existing process, product or service
- Periodically throughout the life of the process, product or service
How Do I Calculate PFMEA?
To accurately calculate your PFMEA score you must first determine the severity of your process. Accendo Reliability does a great job explaining PFMEA severity and has shared the below charts to help you get started identifying how severe the effects of your potential risks are.
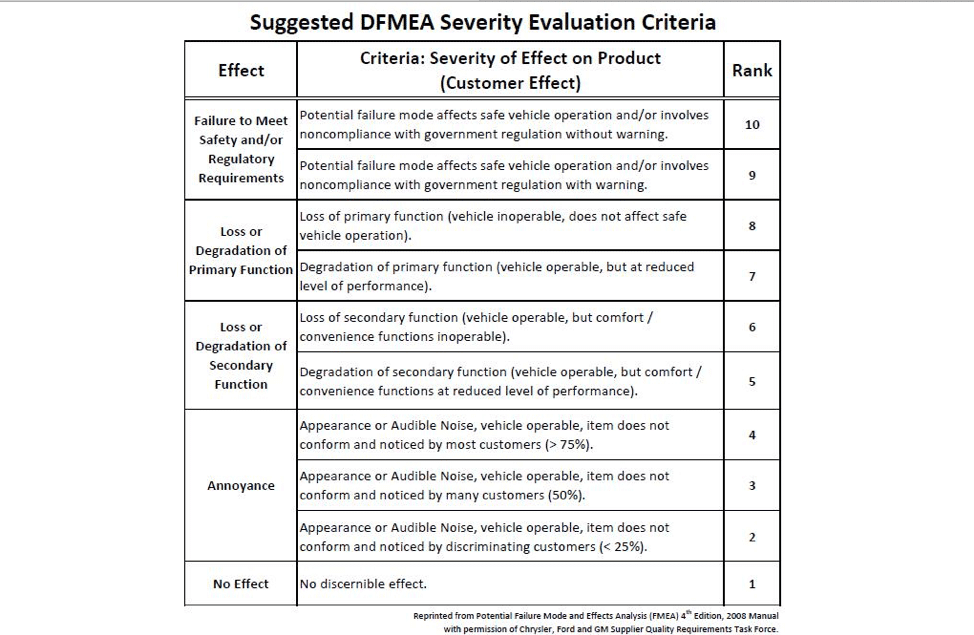
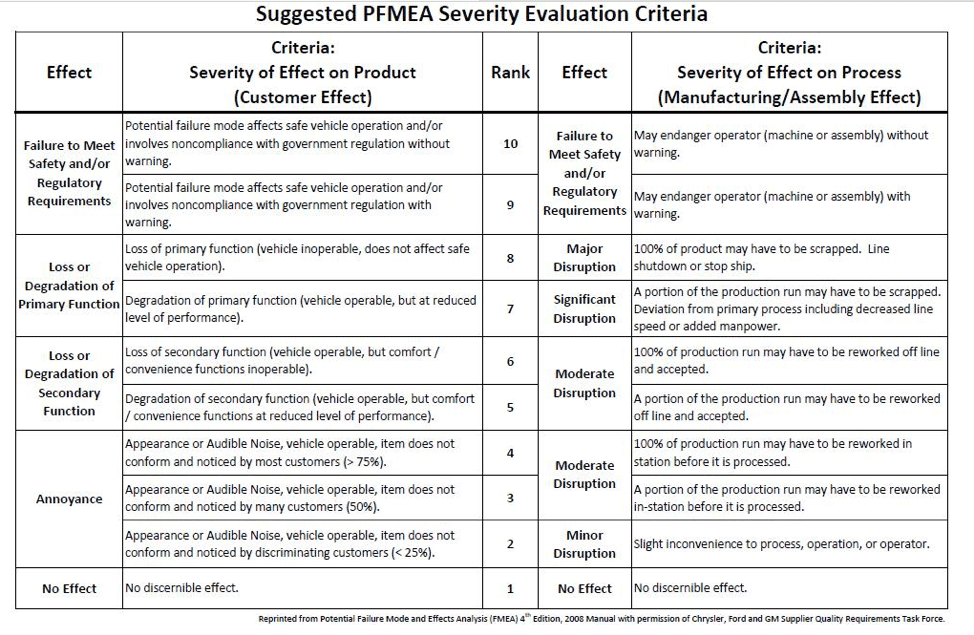
In short, 1 will represent an insignificant error and 10 will mean the severity of the error would be devastating. Next, determine possible root causes for each effect. For each root cause, assign an occurrence rating. Also rated on a scale of 1 to 10, this number represents the probability of failure occurring for that particular cause. For each of the root causes you’ve identified, identify current process controls. These will be the procedures or mechanisms you already have in place to avoid the particular cause. Then, determine the detection rating for each of your controls with 1 meaning your control will definitely detect and solve the problem and 10 meaning the control will definitely not detect the problem or that no control is in place at all.
Once you have defined the potential severity, occurrence and detection probabilities of your process, it’s time to calculate the RPN. To do this, simply multiply your severity, occurrence and detection numbers together, like so:
RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection
For example, if your severity is 7, your occurrence is 2 and detection is 3, your RPN will be 42.
Unless your RPN equals 1 (which is not likely), you will want to decide which changes need to be made to your design or process as well as how urgent those changes are in order to lower your RPN. Even if your overall RPN is low but your severity rating is high, you’ll still want to make changes to the process that would help lower that number. Make sure you note how the changes will be made, such as who will be responsible for any updates and when they need to be made by. After the changes are made, note the results on your FMEA form and calculate your new (hopefully lower!) RPN.
Don’t delay! Download our PFMEA template to start improving your processes today.
Fill out the form below for more information or to contact sales!